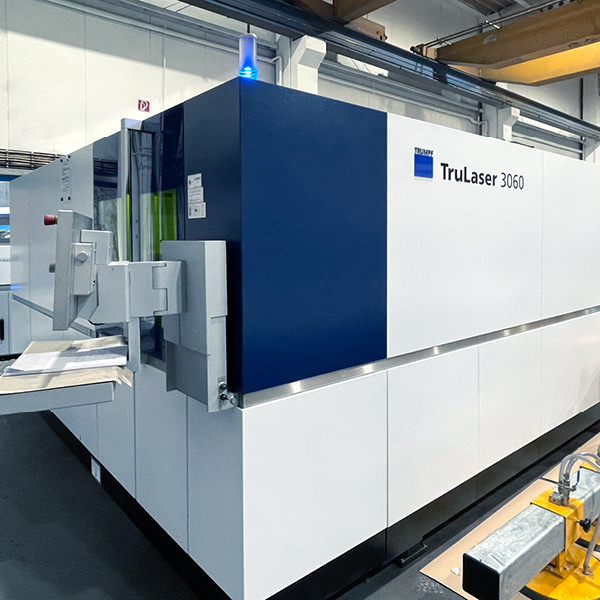
At our company headquarters in Netphen-Deuz (Siegen-Wittgenstein district), we offer our customers the possibility to cut stainless steel oxide-free using state-of-the-art laser technology. Our own laser cutting equipment with a maximum power of 10 kW can process stainless steel sheets with dimensions of up to 6,000 x 2,500 x 20 millimeters.
What is laser cutting?
Laser cutting technology is ideal for producing precise cuts of stainless steel plates in different thicknesses and is distinguished by its versatility. Laser cutting is a highly sought-after method for cutting stainless steel plates up to a thickness of 20 millimetres.
The physical properties of concentrated light beams make them ideal for use as a cutting tool. The laser light's light waves all have the same wavelengths and oscillate at the same frequency. Experts refer to these as monochromatic light waves, which are also coherent. Together with the parallel direction of the light waves, this creates a concentrated light beam with a high power density. A correctly formed laser beam is a powerful cutting instrument for stainless steel due to its high power density.
Laser cutting is a relatively wear-free option for machining stainless steel. This is ultimately also due to the absence of any form of contact in the laser cutting of stainless steel. The high precision of the laser beam means that only local areas on the stainless steel part are exposed to a thermal change in laser cutting – a minimal area of the cutting edge, which is why laser cutting is known to be a method that is particularly gentle on material. The possibility of forming precise contours and cuts also ensures that the rest of the part effectively remains unstressed.
How does a laser cutting machine work?
Put simply, the high concentration of light beams ensures that laser cutting is a powerful method for machining stainless steel. When these concentrated light beams hit the stainless steel material, this point becomes extremely hot. This process takes place extremely quickly and leads to the melting or vaporisation of the material. In laser cutting, the light beam basically penetrates into the stainless steel. The molten metal is blown out to create the kerf, signalling the start of the cutting process. The concentrated beam can them move along the desired contour and create intricate cuts.
What are the benefits of laser cutting?
Laser cutting is perfectly suited for the rapid and precise machining of complex contours as well as for quickly producing high-precision cuts. The low-warpage method of laser cutting ensures that post-processing is normally not necessary. Non-machined areas of the part are not exposed to any thermal load during the laser cutting of stainless steel.
Laser cutting is an efficient method for machining stainless steel. The key benefits of the technology are the processing speed and the precision of the cutting result. Customers also benefit from the freedom from wear and the clean cutting edges.
 und wählen Sie die Option Zum Home-Bildschrim.
und wählen Sie die Option Zum Home-Bildschrim.